Archaeologists have just discovered the oldest Cave Paintings on record in Western Eurasia. These drawings date all the way back 38,000 years. Randall White, the lead archaeologist from New York University, spearheaded the new excavation at the already well establish dig site known as Abri Cellier in Vézère Valley, France. The painting technique discovered is similar to that of modern-day painters. The team's findings were published in Quaternary International.
The Discovery
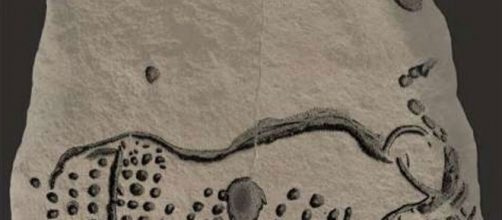
The team discovered 16 limestone blocks that were carbon dated back approximately 38,000 years.
These findings give a sneak peek of Europe's oldest human culture, the Aurignacian. Whoever created these paintings used a series of dots to portray certain images. At least three wooly mammoths are portrayed as well as wild cows (aurochs) and horses. Researchers theorize that these images were painted onto the hand or fingers and then transferred to the stone. This artistic style of painting is similar to the work of modern artists Georges Seurat and Vincent van Gogh. It is reminiscent of the Pointillists and Post-Impressionists styles of painting except it is 38,000 years older! These prehistoric masterpieces are exceptional for their time period and prove that these early humans had an understanding of the fundamentals of shape and lines.
Previous Discoveries
The excavation site at Abri Cellier was first opened back in 1927. Archaeologists had discovered 15 limestone pieces that had been engraved and were thought to be about 38,000 years old as well. However, the oldest example of early human artwork does not come from Europe. It does not even come from Africa. The oldest piece of artwork hails from Indonesia and Australia. The 40,000-year-old, non-figurative art forms discovered in these countries have fascinated archaeologists around the globe. These ancient art pieces were created by blowing paint onto the edges of the hand and pressing the hand onto the stone. This is a very similar technique as the one found in the recent discovery.
The main difference in going from non-figurative painting to characterization via shapes. This is a huge advancement in a 5,000-year time gap. Researchers are continuing to unearth new artistic clues to our past in order to better understand modern humans.