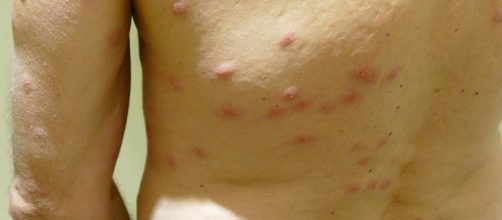
Most insect bites and stings cause temporary discomfort and pain. These insects include mosquitoes, fleas, spiders, ticks, wasps, bees, flies, bedbugs, and beetles.
A child’s reaction to an insect bite or Sting depends on a number of factors such as the location of the bite if toxins are injected and the child’s sensitivity to that insect.According to the Newyork Times, wasp sting is deadlier than even snake or dog bites.
Signs and symptoms of insect bites
- A painful and itchy lesion at the location of the bite or sting
- A larger area of swelling with redness or blisters
Some children may also develop severe anaphylactic reactions that need urgent medical attention.
Its signs include:
- Swelling of the lips and tongue
- Difficulty in breathing and swallowing
- Severe itching and hives
- Fainting
- Coughs, wheezing and choking
- The child becomes pale and floppy
Handling insect bites
- It is essential first to identify the insect that has stung your child to handle the sting properly.
- Bedbugs usually leave a small bite mark on the skin which is red and itchy.
- Bee stings have a red skin bump with white around it.
- Spider bites cause a painful red skin swelling at the site and serious symptoms that need medical care.
- Fleabites usually leave an itchy welt on the legs and ankles.
- Mosquito leaves a raised itchy skin bump.
- Tick bites leave a rash that resembles an expanding bull’s eye and can carry Lyme disease.
A majority of insect bites and stings can be treated at home.
However, bee stings need to be handled carefully by scraping the sting out. If the sting is pinched or pulled, this will cause the toxins to be injected.According to sciencemag.org the DNA of insects have continued to change their brain and body structure affected.
To Treat all bites and stings:
- Wash the skin around the bite using mild soap and water.
- Use an unperfumed moisturizing cream to decrease the itch.
- Apply cool compresses using wet towels for the pain and swelling.
- Administer an oral antihistamine medicine purchased from a pharmacy.
When to see a doctor
Take the child to the doctor for urgent medical care if:
- They display any signs of anaphylaxis.
- The itching and swelling worsen after 24-48 hours.
- The pain does not settle within a few hours.
The doctor may recommend using an adrenaline autoinjector such as EpiPen or an oral steroid such as prednisolone for future bites and stings.
The child should carry all the prescribed medicines all the time.
Prevention measures
To reduce the likelihood of the child getting more bites or stings, follow these simple steps.
- Treat the house carpets, furniture and pets regularly during warmer months to prevent flea infestations.
- Use insect repellent that contains no more than 10 percent of DEET or picaridin.
- Tuck pants into socks and shirts into pants when the children are in wooded areas.