The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) currently has a handful of analog missions worldwide. In an analog study, researchers examine a situation on Earth simulating the physical and mental experiences astronauts face in space.
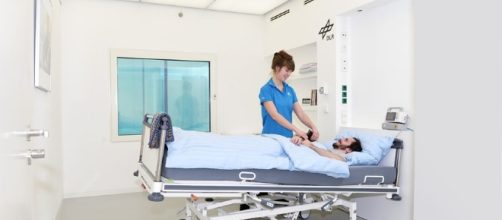
The :envihab (from the words 'environment' and 'habitat') bed-rest study is named after the research facility where the study is planned to take place in this coming September. NASA works together with the Institute of Aerospace Medicine at the German Space Agency DLR for this analog research.
Testing the effects of gravity
Last year in November, NASA's Human Research Program selected a final of four proposals from 10 institutions in 8 states to fund and to be conducted at the designated DLR facility in Cologne, Germany. These are projects focusing on resolving the health and safety risks our astronauts will face in their future missions to Mars and beyond.
According to information on NASA's analog mission page, the bed-rest study investigates visual disorders and brain pressure in astronauts throughout a 60-day period. Subjects are put in a constant Bed Rest with their heads titled in a 6-degree traction. The team wants to get a better understanding of how fluids are distributed in the brain and in the eyes during a simulated space travel.
About the environment and habitat of DLR
The term :envihab is a portmanteau from the words 'environment' and 'habitat'. It refers to a 3500-square-meter space used for exploration in the DLR facility. There are a total of eight separate modules in the design that include special laboratories to study the effects of space on the human body.
It includes a highly specialized PET-MRI analysis facility to conduct positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging as scientist study the physiological changes occurring during long-term missions. NASA plans to have research participants spend 14 days in the acclimatization phase, 30 days of bed rest in a tilted state, and 14 days of rest period.
NASA's human research program overview
The Human Research Program (HRP) at NASA was established in 2005. HRP and the German Aerospace Center DLR have a long history of scientific cooperation and agreements in the aeronautics sector, including in human spaceflight, space explorations, various research areas, and worked together on missions. NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) released a joint research solicitation in November 2015 after selecting four US projects out of the 25 proposals received in response to the call for research made by the agencies.
Good night from #Cologne! pic.twitter.com/Rpa5ttYDsp
— DLR - English (@DLR_en) February 17, 2017
On the bed-rest study section, NASA wrote of one of the critical elements their joint team is trying to understand, "Without gravity pulling blood flow to the legs, astronaut's heads fill with fluids resulting in 'puffy-head, bird-legs' syndrome." Each participant is entitled to €10.000 or about $10,655 of compensation for the study.